Page 21 - South Asia BioBank Sample Health Report
P. 21
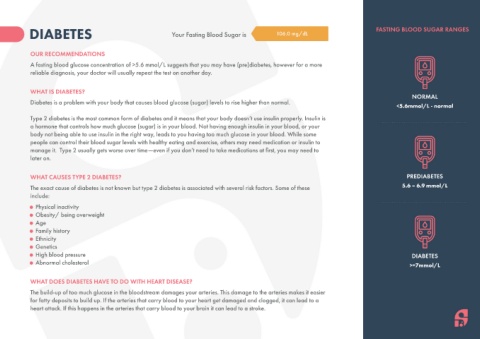
DIABETES Your Fasting Blood Sugar is 106.0 mg/dL FASTING BLOOD SUGAR RANGES
OUR RECOMMENDATIONS
A fasting blood glucose concentration of >5.6 mmol/L suggests that you may have (pre)diabetes, however for a more
reliable diagnosis, your doctor will usually repeat the test on another day.
WHAT IS DIABETES?
NORMAL
Diabetes is a problem with your body that causes blood glucose (sugar) levels to rise higher than normal.
<5.6mmol/L - normal
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and it means that your body doesn’t use insulin properly. Insulin is
a hormone that controls how much glucose (sugar) is in your blood. Not having enough insulin in your blood, or your
body not being able to use insulin in the right way, leads to you having too much glucose in your blood. While some
people can control their blood sugar levels with healthy eating and exercise, others may need medication or insulin to
manage it. Type 2 usually gets worse over time—even if you don’t need to take medications at first, you may need to
later on.
WHAT CAUSES TYPE 2 DIABETES? PREDIABETES
The exact cause of diabetes is not known but type 2 diabetes is associated with several risk factors. Some of these 5.6 – 6.9 mmol/L
include:
Physical inactivity
Obesity/ being overweight
Age
Family history
Ethnicity
Genetics
High blood pressure DIABETES
Abnormal cholesterol >=7mmol/L
WHAT DOES DIABETES HAVE TO DO WITH HEART DISEASE?
The build-up of too much glucose in the bloodstream damages your arteries. This damage to the arteries makes it easier
for fatty deposits to build up. If the arteries that carry blood to your heart get damaged and clogged, it can lead to a
heart attack. If this happens in the arteries that carry blood to your brain it can lead to a stroke.